The Netherlands Enterprise Agency (RVO) has allocated 3.6 million euros to the project SolarEcoPlus. WUR will collaborate on this project with the Netherlands Organization for Applied Scientific Research TNO, and the solar farm developer LC Energy. Among the solar farms to be studied is the one planned on WUR land at the Dijkgraaf. LC Energy aims to create a 10-hectare solar farm there, in combination with research.
Guidelines
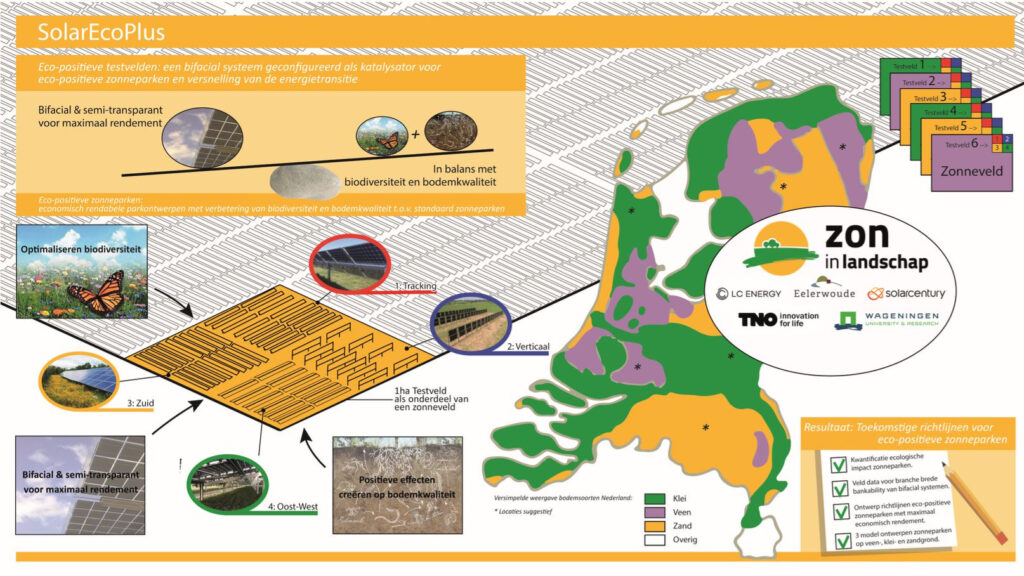
Solar parks are controversial. Their opponents point to their possible negative impact on the soil and vegetation. Because the panels shade the ground, it could dry out and vegetation could shrivel and die. ‘But that is not research-based,’ says WUR project leader Friso van der Zee. ‘This grant enables us to research that. On the basis of the results, we expect to draw up design and management guidelines for improving the ecological quality of solar farms’
‘Herb-rich seed mixes are often used that contain exotic species and varieties’
Friso van de Zee, ecologist and project leader of SolarEcoPlus
To this end, solar farms created according to different designs will be studied. Along with conventional designs, the project will also look at ‘bifacial’ solar panels, which stand upright and capture sunlight on both sides. These panels are expected to score better on ecology, because they stand further apart. Van der Zee says that leaves space to ‘do nice things’.
Squeezed out
One example of what can be done is to reinforce the indigenous vegetation with special seed mixes. Van de Zee: ‘Herb-rich seed mixes are often used that are full of exotic species – from Eastern Europe perhaps. Due to that custom, regional species and varieties get squeezed out, with undesirable consequences. Insects often prefer to forage on particular plants, and exotic species create a mismatch.’
SolarEcoPlus hopes to help conserve local vegetation by collaborating with the Living Archive. The brainchild of Professor Joop Schaminee, the Living Archive aims at safeguarding the genetic diversity of wild plants. ‘The space between the panels could even be used in the long term as a nursery for regional vegetation,’ says Van der Zee. ‘So the seed can be harvested.’
SolarEcoPlus consists of six solar farms on sandy, clay and marshy soils. One of these is the Nergena solar farm – if the plan goes ahead, that is. Ede Municipal Council still has to give the official go-ahead, and there are doubts about whether that will happen. At an earlier stage, the plan was approved by a narrow majority on the Municipality, and one member was absent. The decision is due soon.
Camera traps
The ecological research focuses on a broad spectrum of biodiversity. Van der Zee explains that WUR has developed a monitoring protocol for the research. ‘One aspect of it is monitoring mammals using camera traps. Another is monitoring changes in the soil quality, and we shall look at the effects on the chemical composition and fertility of the soil.’
The project will be implemented over four years. WUR’s research will be funded to the tune of 1.2 million euros.

 Photo: Shutterstock
Photo: Shutterstock 

